How Do You Know You Have Rectal Cancer
Overview
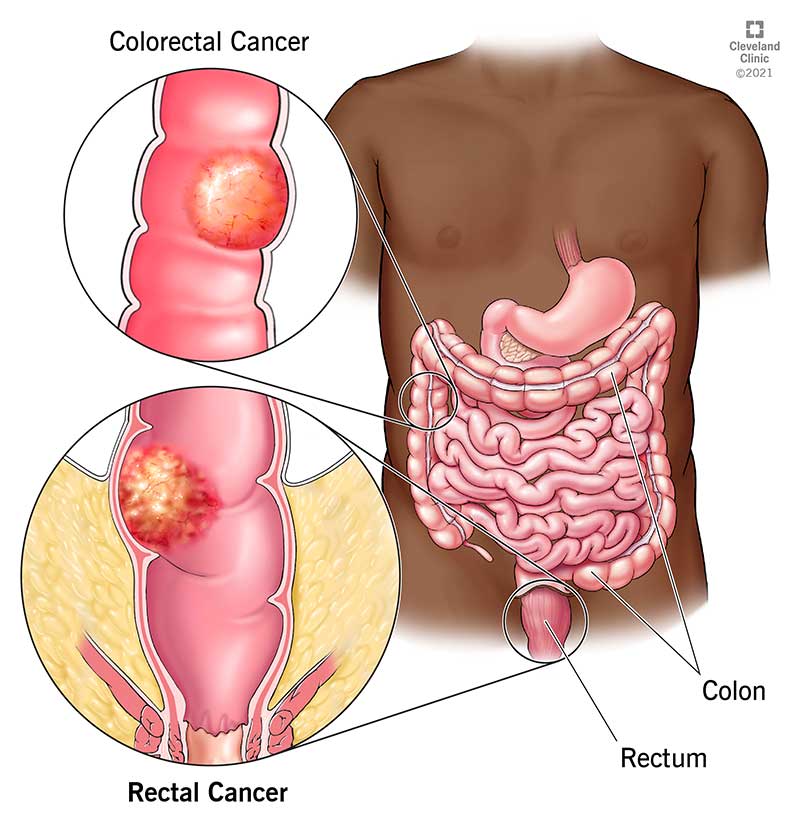
What is rectal cancer?
Rectal cancer develops when cancer cells form in the rectum (the last six inches of the large intestine). The rectum is a chamber that'southward located between the colon and the anus.
Who does rectal cancer touch?
Rectal cancer affects both men and women, though men are slightly more likely to develop the disease. In most cases, people diagnosed with the disease are over the historic period of 50. Yet, information technology's possible for teens and young adults to develop rectal cancer, besides.
How mutual is rectal cancer?
Approximately 5% of people will develop rectal cancer at some point in their lives. Of those people, about 11% will exist nether the age of fifty.
What is the first stage of rectal cancer?
During Stage I, rectal cancer has grown into the deep layers of the rectal wall but has non spread to nearby areas. People with Stage I rectal cancer may non feel any alarm signs or symptoms. That's why routine colonoscopy screenings are so important.
What is the departure betwixt rectal cancer and other cancers affecting the large intestine?
At that place are different types of cancers and diseases that tin affect the rectum. These include:
- Colorectal (colon) cancer : This is a broad term describing cancers of the colon, rectum or both. Colorectal cancer is the third most common course of cancer in the U.South.
- Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) : This condition causes a mutation in an of import cistron — one that'due south inherited or passed downward from a parent to a child. About five% of people with colorectal cancer take HNPCC.
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) : This rare hereditary status causes multiple precancerous polyps to form in the big intestine. People with FAP usually develop polyps in their belatedly teens or early 20s. The polyps become more problematic with historic period, increasing the risk for colorectal cancer.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the warning signs of rectal cancer?
In many cases, rectal cancers don't crusade symptoms at all. However, some people may discover certain warning signs. Rectal cancer symptoms may include:
- Rectal haemorrhage.
- Blood in your stool (poop).
- Diarrhea.
- Constipation.
- A sudden modify in your bowel habits.
- Narrow stool.
- Tiredness.
- Weakness.
- Abdominal pain.
- Unexplained weight loss.
What is the main cause of rectal cancer?
The exact cause of rectal cancer is unknown. Yet, there are certain gamble factors that increase your chance of developing the disease, including:
- Historic period: Like near cancers, the run a risk of rectal cancer increases with historic period. The average historic period of diagnosis is 63 for both men and women.
- Gender: Men are slightly more than probable to develop rectal cancer than women.
- Race: Statistically, Blackness individuals are more probable to develop rectal cancer. The reasons for this aren't fully understood yet.
- Family history: If you have a family member who has been diagnosed with rectal cancer, your gamble of developing it is almost double.
- Certain diseases and conditions: There are several health weather condition that can increment your risk for rectal cancer, including inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Smoking : Contempo research suggests that people who smoke are more than likely to dice from rectal cancer than people who don't.
- Eating candy meat: People who eat a lot of crimson meat and processed meat have a higher run a risk of developing rectal cancer.
- Obesity: People with obesity are more likely to have rectal cancer compared to people who are considered a healthy weight.
Experts recommend that all people have routine colorectal screenings get-go at age 45. People who have a higher risk of rectal cancer should undergo more frequent screenings. Find out more about general cancer screening guidelines recommended by healthcare providers.
What should I know nearly rectal cancer staging?
Rectal cancer is categorized into five different stages. Your diagnosis depends on how large the rectal cancer tumor is and whether or non it has spread:
- Stage 0: Cancer cells have been found on the surface of the rectal lining.
- Stage 1: The tumor has grown below the lining and possibly into the rectal wall.
- Phase two: The tumor has grown into the rectal wall and might extend into tissues around the rectum.
- Phase 3: The tumor has invaded the lymph nodes next to the rectum and some tissues exterior of the rectal wall.
- Stage 4: The tumor has spread to distant lymph nodes or organs.
How does rectal cancer spread?
If you lot have Phase 4 metastatic rectal cancer, it means that the cancer has spread across the rectum into other areas of the body. While it'south possible for these cancer cells to travel anywhere in your trunk, they're more likely to finish up in the liver, lungs, brain or abdominal lining.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is rectal cancer diagnosed?
Most cases of rectal cancer are diagnosed during routine screenings. In some instances, your provider may suspect the affliction based on your symptoms.
What tests will be done to diagnose rectal cancer?
If your healthcare provider thinks yous could have rectal cancer, they may order some tests to ostend your diagnosis. These tests may include:
- Colonoscopy : This test uses a long tube with a small camera to view the inside of your colon and rectum.
- Biopsy : Your healthcare provider takes a pocket-sized sample of suspicious tissue and sends it to a lab for analysis.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan : This imaging test takes X-rays of your body, then stitches them together for a detailed view of your bones, organs and tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) : Unlike Ten-rays, MRI uses radio waves and magnets to capture images inside your trunk.
- PET browse (positron emission tomography): Earlier having a PET scan, your healthcare provider asks y'all to potable a special dye that contains radioactive tracers. (In some cases, the dye may be injected or inhaled.) The dye highlights areas of affliction.
Management and Treatment
How is rectal cancer treated?
Rectal cancer handling depends on several factors, including the location, size and stage of your tumor, as well every bit your overall health and personal preferences. Options include:
Surgery
One of the about common rectal cancer treatments, surgery removes cancer cells. There are a few different surgical options based on your specific needs:
- Transanal endoscopic microsurgery (TEMS) : During this procedure, your surgeon removes minor cancers from the rectum using a special scope inserted through your anus. This treatment is recommended if your tumor is small, contained to 1 area and unlikely to spread.
- Low anterior resection: Larger rectal cancers may require total or partial removal of the rectum. The anus is preserved and then that waste can leave your trunk unremarkably.
- Abdominoperineal resection (APR) : When cancer is located near the anus, it may non be possible to remove information technology without damaging the muscles that control your bowel movements. In this case, your surgeon may remove the anus, rectum and part of the colon. A colostomy is then performed so that waste material can leave your body. (During a colostomy procedure, your surgeon creates an opening, or stoma, in your abdomen. The end of your colon is then attached to the opening and stitched into place. When waste product leaves your body, it'south collected in a pocketbook that's connected to the stoma.)
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used earlier surgery to shrink a tumor, or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Radiation therapy
Like chemotherapy, radiations therapy may be used before or after surgery. Radiation therapy uses potent free energy beams to impale cancer cells or go along them from growing and dividing. It can exist used in combination with chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy uses drugs to heave your immune system and teach your body how to assault cancer cells.
Targeted drug therapy
If you lot have avant-garde rectal cancer, your oncologist may recommend targeted drug therapy in combination with chemotherapy. These treatments target specific abnormalities in the cancer cells, causing them to die.
What are the complications of rectal cancer treatment?
Complications can vary depending on which blazon of rectal cancer treatment you receive. Additionally, every person'due south experience may be different. Merely considering someone else had certain complications doesn't mean that you will accept them also. Tiredness, weight changes, nausea/vomiting and diarrhea are the well-nigh common side effects during about rectal cancer treatments.
Prevention
Can rectal cancer be prevented?
While you can't preclude rectal cancer birthday, there are steps you tin can take to reduce your hazard. For example:
- Stay at a good for you weight.
- Practice regularly.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
- Avert drinking alcohol.
- Don't smoke.
Outlook / Prognosis
Tin can you survive rectal cancer?
Aye. When detected and treated early, rectal cancer tin be successfully cured.
What'due south the rectal cancer survival rate?
The overall 5-year survival rate for rectal cancer is 63%. This means that people who have rectal cancer are almost 63% as likely to exist alive in v years every bit people who don't have rectal cancer. The five-twelvemonth survival rate for localized rectal cancer (that hasn't spread to other areas of the torso) is 91%. This means that people who accept early stage rectal cancer are about 91% as probable to be live in five years as people who don't have rectal cancer.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates based on people who have had rectal cancer in the by. They tin can't predict what will happen or how long y'all will live. To learn more about rectal cancer survival rates, talk with your healthcare provider.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you're undergoing rectal cancer treatment, call your healthcare provider correct away if you develop:
- A fever of 100.iv° or college.
- Astringent headaches.
- Chills.
- Blood in your pee.
- Breast pain.
- Shortness of jiff (dyspnea).
- Confusion.
You know your body best, so trust your gut. If something doesn't seem quite correct, make an appointment with your healthcare provider. They tin can find ways to ease your symptoms and help you experience ameliorate.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
If you've been diagnosed with rectal cancer, you'll want to gather as much information as you can. Hither are some questions to ask your healthcare provider:
- What stage of rectal cancer practice I take?
- How far has the cancer spread?
- What are my treatment options?
- How will treatment affect my quality of life?
- Will I exist able to work during treatment?
A annotation from Cleveland Clinic
Being diagnosed with rectal cancer can be overwhelming. You may feel sad, scared, frustrated or angry. Ask your healthcare provider about resource that can assist you navigate this hard time. You lot may also want to consider joining a support group for people with rectal cancer. Noesis is power. Having a full understanding of your diagnosis and handling options tin empower you and aid you take back control of your health.
Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21733-rectal-cancer
0 Response to "How Do You Know You Have Rectal Cancer"
Post a Comment